What Is the Intelligent Edge?
The intelligent edge refers to the practice of adding greater compute capacity at the network where data is generated, enabling local collection, analysis, and actions based upon that data.
Relationship with Embedded Systems
Intelligent edge architectures are complementary to embedded systems, bringing scalable compute nearer to resource-constrained embedded systems and enabling these systems to leverage more complex, more compute-intensive processes (including machine learning), as well as local processing of historical data. While Internet of Things (IoT) topologies routinely depict a round-trip journey for data from edge devices to the cloud for processing and then back, this approach can be costly and take time that a system with real-time requirements simply doesn’t have. The intelligent edge eliminates that journey, moving compute power from the cloud to the edge.

“Intelligent edge” refers to the practice of moving compute power to to the edge of the network, where devices are generating data.
Differences Between the Intelligent Cloud and the Intelligent Edge
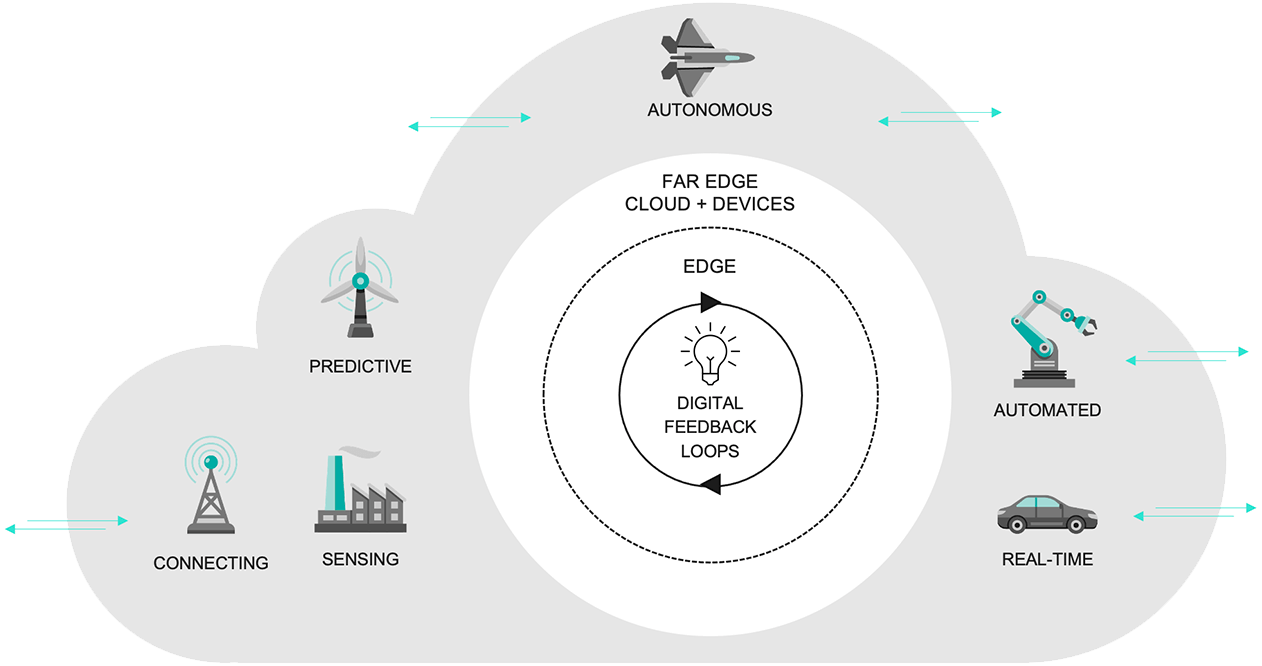
The intelligent edge and mission-critical intelligent systems
The intelligent edge contrasts with highly centralized cloud-oriented architectures in which systems at a network’s edge send data to the cloud. In the early days of IoT, devices had few edge processing capabilities, and consequently a lot of raw data was sent to the cloud. While this provided a central place for processing to occur, it also created high operational costs.
With the intelligent edge, intelligence is being incorporated at the device level. Instead of processing all that data in the cloud, data interpretation is now being done on the intelligent device itself, which then sends metadata to the cloud. The cloud can process this data more consistently and at a much lower operational cost.
To scale the operation of multiple edge devices, the central cloud location will need to monitor the performance of those devices.
For efficient operation, one person will need to be able to monitor thousands or millions of devices at a time — meaning that the edge devices themselves must be able to discover any anomalous behavior.
When an anomalous action is spotted, an operator is notified that a device is breaking, so they can keep their solution up and running.
By adding scalable compute near resource-constrained or fixed-function devices generating data, systems in an intelligent edge architecture can engage in more timely, more selective, and less costly interactions with that data, while also reducing security risks.
Use Cases for the Intelligent Edge
Connectivity
Intelligent edge devices are necessarily connected. Connectivity can include connections between devices, local compute resources, and the internet. This contrasts with devices and systems that are air gapped for security reasons, or that were developed and deployed with no connection to either the internet or an internal network. To deliver on intelligent edge capabilities, such legacy or purpose-built systems can be enhanced with connectivity through solutions sometimes referred to as “bolt-on.”
Compute
Intelligent edge devices are often resource constrained by design. Such fixed-function systems are highly optimized for performance (speed, reliability, safety) as well as cost, with designs that consume available compute resources down to the last clock cycle.

Intelligent edge devices are necessarily connected and often resource constrained by design.
Intelligent edge architectures supplement the compute capacity of these systems by adding scalable compute resources in close proximity.
Control
By making additional compute resources available to these systems, intelligent edge deployments enable diverse sorts of decision-making to take place in the local environment. These include system-level optimizations across devices, changes to the programming of specific devices, and other forms of control.
Applications of the Intelligent Edge

Intelligent edge systems must be able to process information instantly, with no lag time even in the event of network failure.
Aerospace and Defense
The intelligent edge enables warfighters to continue to access available information in the event of a network failure, rather than experiencing lag in decision-making or operating without that vital information. When warfighters become disconnected, they can operate offline and batch changes at the edge, then connect back to the network when possible.
Automotive
Services such as dynamic high-precision 3-D maps and intelligent driving rely on the network’s ability to instantaneously process localized data and transmit actionable insights. Mobile networks will need their computing resources to process the right data in the right place at the right time: a topology-aware distributed edge computing cloud architecture.
Healthcare
Currently, monitoring devices (e.g., glucose monitors and other sensors) are either not connected or, if they are, large amounts of their unprocessed data need to be stored on a third-party cloud. This presents security concerns for healthcare providers. Instead, an edge on the hospital site could process data locally to maintain data privacy. Through analytics and AI, the edge also enables right-time notifications to practitioners about unusual patient trends or behaviors and the creation of patient dashboards that include more comprehensive current and historical data.
Industrial
The intelligent edge enables deployment of digital twins on factory floors and in other industrial settings. Technical and business benefits over cloud-based digital twins include latency low enough for use in mission-critical applications, closed-loop integration of analytics, and local control functions resulting in faster response times for such event-based operations as safety shutoff. Ultimately it will also enable faster evolution of the digital twin.
The Future of the Intelligent Edge
To a degree, the future of the intelligent edge is now, bringing the compute capacity required to enable autonomous driving use cases, artificial intelligence, and other compute-intensive processes to the operational technology domain. Ultimately, the distinction between core and edge will become less relevant as the compute required to deliver on intelligent edge use cases and the connectivity required to meet unique real-time safety and security requirements of diverse embedded systems become increasingly ubiquitous across distributed architectures.
Benefits of Computing at the Intelligent Edge
Improving Latency and Bandwidth
The application-specific considerations of latency of mission-critical systems are particularly demanding. By reducing both the amount of data passing over a network and the amount of time that data spends in motion, computing at the intelligent edge can reduce overall latency.
Security Threats
By processing data from systems and delivering updated functionality and instruction sets to those systems, local applications leveraging intelligent edge architectures can limit exposure to security threats. However, carriers introducing the compute resources required to deliver on 5G intelligent edge use cases are placing equipment in environments that are less controlled than centralized data centers or network operations centers.
Wind River Solutions That Power the Intelligent Edge
Wind River Studio
Wind River® Studio is the first cloud-native platform for the development, deployment, operations, and servicing of mission-critical intelligent edge systems that require security, safety, and reliability. Studio provides a unified set of development, security, and operations pipelines so you can connect your mission-critical edge devices to the cloud and build products and releases.
>> Learn moreVxWorks
Today billions of edge devices run on VxWorks®. Bringing intelligent edge capabilities to these devices, as well as to the next generation of design wins in the markets we serve, is a key focus for Wind River. That’s why VxWorks is the only RTOS to support C++17, Boost, Rust, Python, pandas, and more, as well as an edge-optimized, OCI-compliant container engine.
>> Learn moreWind River Linux
Open source Linux is the default environment for developing embedded solutions for the intelligent edge. Wind River Linux provides the industry’s most advanced embedded Linux development platform, with a comprehensive suite of products, tools, and lifecycle services to help our customers build and support intelligent edge devices in segments such aerospace and defense, industrial, medical, automotive, and more. Wind River provides an offering to keep your code base up-to-date, track and fix defects, apply security patches, and customize your runtime to adhere to strict market specifications and certifications. Additionally, Wind River can facilitate your intellectual property and export compliance and significantly reduce your OpEx costs.
>> Learn morePersonalized, Outcome-Driven Services
Wind River expertise in delivering services can match your unique business needs, helping you move from your current environment to the achievement of your goals. We can create custom solutions by integrating our products with third-party, open source, and custom software and hardware.
>> Learn moreWIND RIVER CUSTOMER SUCCESS MANAGEMENT
Enablement Services
Onboarding, installation, and workflow optimization
Acceleration Services
Improved adoption by integrating with customer tools and the development environment
Transformation Services
Business outcome-driven approach, managed services or fleet
Dedicated Support
Elevated support experience
Engineering Access
Access to SMEs, product strategy influence
eLearning
Access to the Wind River Learning Subscription and Knowledge Forum
Customization and Transformation Services
We provide board support package/flexible software package (BSP/FSP), boot optimizing, security hardening, and system integration services.
Certification and Compliance Services
If you are in a regulated industry, your operating system, BSP, application, and/or entire system will probably need to be certified to mitigate risk. The process of certification is long and complex, and Wind River is one of few companies that can help address certification from start to end.
Full Lifecycle Services
Wind River expertise in mission-critical functionalities, skill sets, and risk mitigation in intelligent systems can ensure that your system stays protected against all security vulnerabilities and is bug free, with all monitoring, analysis, and mitigation completely managed for you.
Assessments
We can provide a variety of assessments to derive solutions, security, and ROI to help reduce risk and cost.



